MIT-6.830 Lab1 总结与备忘
SimpleDB由以下部分组成:
代表字段、Tuple和Tuple模式(tuple schemas)的类
- Fields是字段属性接口,包含FileName和FileType,其中FiledType目前仅支持Int和String
- Tuple一条记录,包含TupleDesc、RecordId和FiledList属性
- TupleDesc是Tuple的属性,存储Tuple的相关Field信息
- Page是读入内存的数据页面,磁盘里的数据页称作页块,PageId作为主键,PageSize存储在BufferPool中。SimpleDb中包含了两类page:
- HeapPage,存放于HeapFile中
- BTreePage
- PageId为Page的识别码,有TableId、pageNumber属性。TableId根据文档描述暂时指定为DbFile.Id,每个Table可能有多个Page共同存储数据;pageNumber标识当前页在磁盘file中的相对位置
对Tuple应用谓词和条件的类。
一个或多个访问方法(例如,堆文件),将关系存储在磁盘上,并提供一种方法来遍历这些关系的Tuple
SimpleDb中,每个table对应一个DBFile
HeapFile是DBfile的一种实现,是一种顺序文件,一个HeapFile对象由一系列固定大小的连续HeapPage构成
HeapPage:
- HeapFile中由一些列的插槽(slot)组成,每一个插槽可以存放一个tuple。在一张表中的tuple所占大小相同
- 有一个bitmap存放slots是否有tuple信息,方便数据访问操作
HeapPage在HeapFile中按顺序存放,依据HeapPage.PageId.PageNumber快速定位HeapPage在HeapFile中的位置
HeapPage的信息由header + actual content构成,header的大小由tupleSize和pageSize共同决定;一个tuple需要tupleSize字节存真实数据, 以及一个bitmap中的标识位:
1
2tupleNumber = Math.floor(pageSize * 8 / (tupleSize * 8 + 1));
headerSize = Math.ceil(tupleNumber / 8);
一个操作类的集合(例如,选择、连接、插入、删除等),用于处理Tuple。
一个缓冲池,用于缓存内存中的活动Tuple和Page,并处理并发控制和事务(在本实验中你不需要担心这两点)
- 所有读Page的操作均需要从BufferPool经过,DataBase全局仅有一个缓冲池实例
- 缓冲池大小由属性numPages决定
- BufferPool需要实现事务请求页面的加锁处理、死锁检测、页面换入换出等功能
一个 catalog ,存储数据库元信息(metadata),比如table
SimpleDB没有实现视图
要理解Table、Page以及HeapFile的关系,即看到的Table、内存的Page、磁盘的File是如何交互的——数据库中的block对应HeapFile,在内存中数据以Page为单位存储
Lab1除了顺序扫描外,不需要实现其他操作符(select、join等)
Exercise 1
思路整理
Implement the skeleton methods in:
src/java/simpledb/storage/TupleDesc.java、src/java/simpledb/storage/Tuple.java,通过单元测试TupleTest和TupleDescTest一个Tuple对象表示一行数据
- 包含TupleDesc、RecordId和fieldList属性
Tuple由Field组成,Field为储存数据的单位
一个TupleDesc对象表示数据的表头
- 有一个TDItem队列,TDItem表示一个属性,其中有 fieldType 和 fieldName 两个字段
- 例如学生的姓名属性,fieldName是姓名,fieldType是字符串
fieldType,这是一个 Type 对象,分为INT_TYPE和STRING_TYPE类型
Field是一个接口,实现了String和Int
具体实现(包括java的一点实践记录)
import java.util.ArrayList- ArrayList是动态的数组(是一个模板),而另一个包Array是静态的数组
- ArrayList的增删改查:
add(element),remove(int Index),set(index, element),get(int index)
StringBuilder:- String内容是不可变的,StringBuilder内容是可变的
- 常用方法:
length()、append、setCharAt(int index, element)、insert(int index, element)、delete(int fromIndex, int toIndex)(前闭后开)
- 具体实现过程,理解两个类分别代表什么含义,然后根据相应函数上方的提示完成即可
Exercise 2
思路整理
- Implement the skeleton methods in:
src/java/simpledb/common/Catalog.java,通过单元测试CatalogTest - Catalog:
- 实现一个Table内部类,Catalog要维护多张表
- Table类:
- 表示一张表
- 类似TDItem,包含file,name,pkeyField三个字段,pkeyField表示主键,name表示表的名字,file是一个DbFile对象
- Table类:
- 用HashMap来维护,
key: file.getId(),value:Table - 对于重名table,删除该table再重新添加
- 实现一个Table内部类,Catalog要维护多张表
- DbFile为数据库磁盘文件的接口,可由HeapFile和B+树实现,目前是HeapFile,其中存储了很多Tuple,数据库中每张表对应着一个DbFile,DbFile储存着表中的所有信息(Exercise 3有更具体的说明)
具体实现
Hashmap:
加入元素:
put(key, value)遍历:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public void addTable(DbFile file, String name, String pkeyField) {
// some code goes here
Table curTablle = new Table(pkeyField, name, file);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Table> entry: this.tables.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().getName().equals(name)) {
this.tables.remove(entry.getKey());
break;
}
}
this.tables.put(file.getId(), curTablle);
}是否存在键:
containsKey(key)
注意在
addTable的时候,检查table的name是否重合,如果重合则删除旧的table再add
Exercise 3
思路整理
Implement the skeleton methods in:
src/java/simpledb/storage/BufferPool.java,无单元测试,在HeapFile的实现中测试缓冲池负责在内存中缓存最近从磁盘读取的Page,操作者通过缓冲池从磁盘上的各种文件读写Page。缓冲池由固定数量的页面组成——
numPages参数定义,本实验中如果对不同页面的请求超过numPages,可以抛出一个DbException。之后的实验会要求实现一个替换策略,本lab只需要实现构造函数和SeqScan操作所需要的BufferPool.getPage()Database类提供了一个静态方法
Database.getBufferPool(),用于返回整个SimpleDB进程的单个BufferPool实例的引用ConcurrentHashMap——HashMap 存在并发问题——来存page,key和value分别是PageId和Page
getPage()- 根据PageId查询内存缓存中是否有对应页面,若有执行3,否则进行2
- 如果当前缓存的页数等于
numPages,抛出- 一个DbException。否则,根据PageId.TableId在Catalog中获取DbFile,在DbFile中依据PageId.PageNumber从磁盘读取页面,将读出的页面放入缓存
- 将结果返回
DbFile:
- 接口实现向磁盘读写page、向Page插入删除tuple等功能
- 一个DbFile存一个table ,数据库中的Table和DbFile是对应的
- HeapFile是DbFile的一种实现(还有B-tree实现)——HeapFile access method
- HeapFile存了一个Page集合,每个页面由固定数量的字节组成
- HeapPage是Page的一种实现,每一个page都存有固定数量(
BufferPool.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE)的 tuple
- HeapFile每一页都有一组槽(slot),每个slot“嵌入”一个tuple
- 每个page还有head 部分,记录page中的slot是否被使用
数据库中的block对应HeapFile,在内存中数据以Page为单位存储
具体实现
多线程环境下,使用Hashmap进行put操作会引起死循环——所有访问HashTable的线程都必须竞争同一把锁
ConcurrentHashMap:
- 使用锁分段技术,将数据分成一段一段的存储,给每一段数据配一把锁,当一个线程占用锁访问其中一个段数据的时候,其他段的数据也能被其他线程访问
- ConcurrentHashMap可以做到读取数据不加锁
- 由Segment数组结构和HashEntry数组结构组成
- Segment是一种可重入锁ReentrantLock,在ConcurrentHashMap里扮演锁的角色。Segment的结构和HashMap类似,是一种数组和链表结构, 一个Segment里包含一个HashEntry数组,每个HashEntry是一个链表结构的元素, 每个Segment守护着一个HashEntry数组里的元素,当对HashEntry数组的数据进行修改时,必须首先获得它对应的Segment锁
- HashEntry用于存储键值对数据
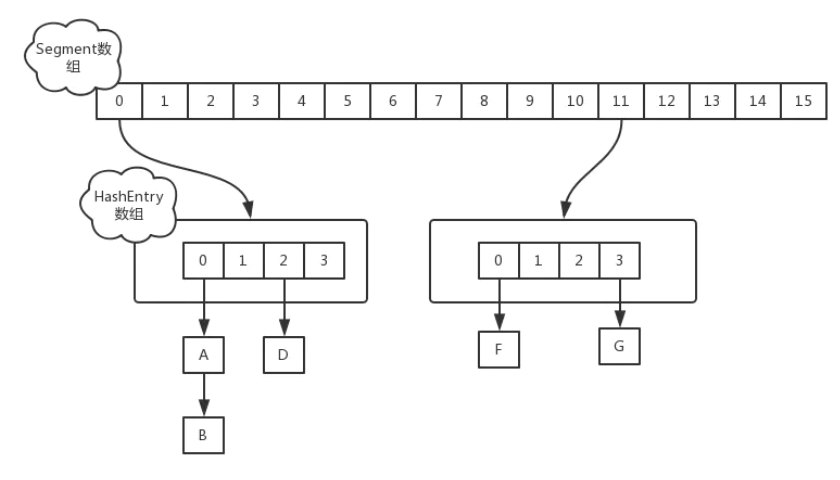
综上,需要新增两个属性:
numPage和ConcurrentHashMap<PageId, Page> mapgetPage()1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public Page getPage(TransactionId tid, PageId pid, Permissions perm)
throws TransactionAbortedException, DbException {
// some code goes here
Page curPage = this.map.get(pid);
if (curPage == null) {
if (this.map.size() == this.numPages) {
throw new DbException("BufferPool is full...");
} else {
this.map.put(pid, Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(pid.getTableId()).readPage(pid));
}
}
return curPage;
}
Exercise 4
思路整理
Implement the skeleton methods in:
src/java/simpledb/storage/HeapPageId.java、src/java/simpledb/storage/RecordId.java、src/java/simpledb/storage/HeapPage.java,代码应该通过HeapPageIdTest、RecordIDTest和HeapPageReadTest单元测试HeapFile中存了一组Page ,Page中存tuple 。数据库中一张table对应一个Heap File
HeapFile分为head和slot,slot对应一个tuple,注意此处的tuple长度相同。head则是bitmap ,表示slot是否被使用,0表示没有被用, 1表示已经被使用
1
_tuples per page_ = floor((_page size_ * 8) / (_tuple size_ * 8 + 1))
- 其中
_page size_ * 8表示一页需要多少二进制位,_tuple size_ * 8 + 1表示一个 tuple 占多少二进制位。除此之外,一个 tuple 存在与否也占一个二进制位,所以加一。二者做除法就是一页可以存放多少 tuple - 根据页面的 tuple 数字可以确定 bitmap 的个数:
headerBytes = ceiling(tupsPerPage/8)
- 其中
HeapPageId和RecordId即完成构造函数和getter
bitmap的get操作,需要做一个从原始序号到bitmap序号的映射
具体实现
A RecordId is a reference to a specific tuple on a specific page of a specific table,因此RecordId有属性
HeapPageId有属性
int tableId和int pageNo要注意header为一个bitmap(一个字节存8个),因此给定一个index去查该index的slot是否被使用时,需要转换为bitmap的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6public boolean isSlotUsed(int i) {
// some code goes here
int bytes = i/8;
int bits = i%8;
return ((header[bytes] >> bits) & 1) == 1;;
}实现哈希:
1
2
3import java.util.Objects;
Objects.hash(x, y); // 基于x和y的哈希(后面可以继续加)
Exercise 5
思路整理
Implement the skeleton methods in:
src/java/simpledb/storage/HeapFile.java,通过HeapFileReadTest的单元测试从磁盘上读取一个页面时,需要计算出Page在文件的偏移量(此时不应该调用BufferPool方法)
还需要实现
HeapFile.iterator()方法,应该遍历HeapFile中每个页面的 tuple 。迭代器必须使用BufferPool.getPage()方法来访问HeapFile中的页面——将页面加载到缓冲池中,用于后面实验中实现基于锁的并发控制和恢复。 不要在open()调用时将整个表加载到内存中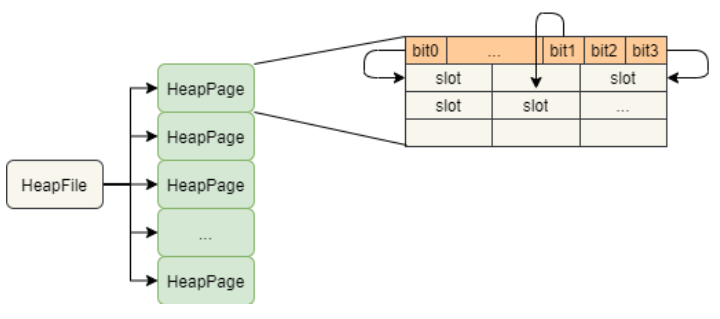
具体实现
readPage需要结合RandomAccessFile实现,由PageId.PageNumber + BufferPool.PageSize确定offset,读入字节数据data,将data传递给HeapPage构造方法返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public Page readPage(PageId pid) throws IOException {
// some code goes here
int pageNo = pid.getPageNumber();
int pageSize = BufferPool.getPageSize();
try {
RandomAccessFile curFile = new RandomAccessFile(this.file, "r");
byte[] data = new byte[pageSize];
curFile.seek((long) pageNo * pageSize);
curFile.read(data);
HeapPage curPage = new HeapPage(new HeapPageId(pid.getTableId(), pid.getPageNumber()), data);
curFile.close();
return curPage;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}iterator需要返回HeapFile中tuple的迭代器——iterator的返回对象可以通过继承DbFileIterator接口实现——要求不停读入页面,此时iterator读入页面时需要调用BufferPool.getPage,而BufferPool.getPage又会调用HF.readPage,然后再从Page中读入tuple。因此内部还有Page.iterator,并根据id更换Page。其中的
open()是打开一个page,hasNext()判断当前的File是否还有tuple1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75public class HeapFileIterator implements DbFileIterator {
private int curPageNo;
private int pageNum;
private Iterator<Tuple> iterator;
private HeapFile heapFile;
private TransactionId tid;
public HeapFileIterator (HeapFile heapFile, TransactionId tid) {
this.heapFile = heapFile;
this.tid = tid;
this.curPageNo = 0;
this.pageNum = heapFile.numPages();
}
public Iterator<Tuple> getNextPage(HeapPageId id) throws TransactionAbortedException, DbException {
BufferPool pool = Database.getBufferPool(); // 从bufferpool中读取page,如果没有再从磁盘读(getPage中有判断)
HeapPage page = (HeapPage) pool.getPage(this.tid, id, Permissions.READ_ONLY);
return page.iterator();
}
public void open() throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
this.curPageNo = 0;
HeapPageId pageId = new HeapPageId(this.heapFile.getId(), 0); // table和HeapFile一一对应
this.iterator = this.getNextPage(pageId);
}
public boolean hasNext() throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
if (this.iterator == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.iterator.hasNext()) {
return true;
} else {
for (int i = this.curPageNo; i < this.pageNum; i++) {
this.curPageNo += 1;
this.iterator = this.getNextPage(new HeapPageId(this.heapFile.getId(), this.curPageNo));
if (this.iterator == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.iterator.hasNext()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
public Tuple next() throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException, NoSuchElementException {
if (this.iterator == null || !this.iterator.hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return this.iterator.next();
}
public void rewind() throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
this.curPageNo = 0;
this.close();
this.open();
}
public void close() {
this.curPageNo = 0;
this.iterator = null;
}
}RandomAccessFile:
- Java 输入/输出流体系中功能最丰富的文件内容访问类,可以从任意位置访问文件
Exercise 6
思路整理
Implement the skeleton methods in:
src/java/simpledb/execution/SeqScan.java,完成ScanTest系统测试SimpleDB中,操作符是基于迭代器的——操作符都实现了
DbIterator接口操作符通过将低级别的操作符传递到高级别的操作符的构造器中,即“chain them together”。 Special access method operators at the leaves of the plan are responsible for reading data from the disk. 和SimpleDB交互的程序只需在根操作符上调用
getNext,从而根操作符在其子操作符上调用getNext,以此类推,直到调用叶操作符从磁盘中获取 tuple ,作为getNext的返回参数向上传递
SeqScan从构造函数的
tableid指定的表中的页面,顺序扫描所有 tuple。这个操作符应该通过DbFile.iterator()(DbFileIterator)访问tuple——即上一个exercise实现的HeapFile.iterator来访问(next、hasnext等),时刻记住DbFileIterator是一个接口
具体实现
1 | private TransactionId tid; |
修改HeapFile中的hasNext()——否则,无法通过测试中的testCache(),Counts the number of readPage operations,总是会多一次。
1 |
|
总结:
Catalog 中有多个table,一个table对应一个DbFile,HeapFile中存了多个Page,一个Page中有一个head和多个slot ,一个slot存一个tuple
HeapFile是DbFile的一种实现方式,除此之外还有BTreeFile
BufferPool保存缓存的Page,需要更新Page时,从HeapFile中查找并更新
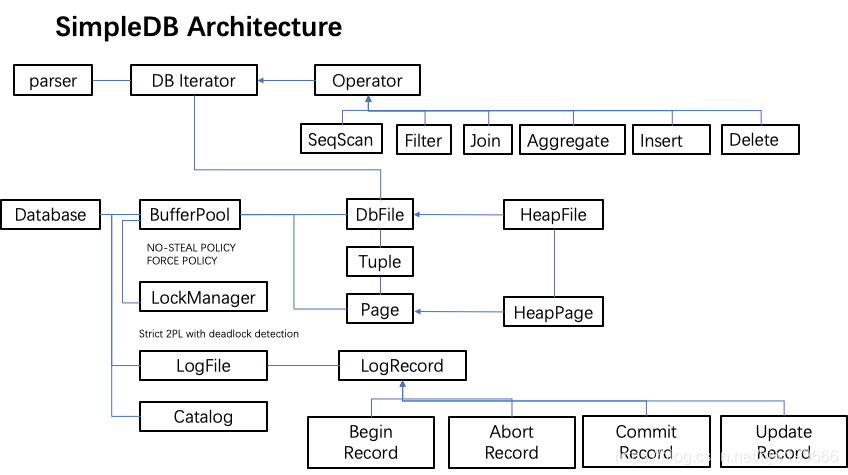
(本图来自https://www.cnblogs.com/cpaulyz/p/14606606.html)
补充:一个具体的查询过程
假设有一个数据文件”some_data_file.txt”,内容如下:
1
2
31,1,1
2,2,2
3,4,4转换为SimpleDB查询的二进制文件:``java -jar dist/simpledb.jar convert some_data_file.txt 3`,“3”表明输入有三列
具体查询代码为(
SELECT * FROM some_data_file)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37package simpledb;
import java.io.*;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
// construct a 3-column table schema
Type types[] = new Type[]{ Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE };
String names[] = new String[]{ "field0", "field1", "field2" };
TupleDesc descriptor = new TupleDesc(types, names);
// create the table, associate it with some_data_file.dat
// and tell the catalog about the schema of this table.
HeapFile table1 = new HeapFile(new File("some_data_file.dat"), descriptor);
Database.getCatalog().addTable(table1, "test");
// construct the query: we use a simple SeqScan, which spoonfeeds
// tuples via its iterator.
TransactionId tid = new TransactionId();
SeqScan f = new SeqScan(tid, table1.getId());
try {
// and run it
f.open();
while (f.hasNext()) {
Tuple tup = f.next();
System.out.println(tup);
}
f.close();
Database.getBufferPool().transactionComplete(tid);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println ("Exception : " + e);
}
}
}表有三个整数字段,为描述这一信息,创建一个
TupleDesc对象,并传递给它Type对象数组和String字段名数组创建
TupleDesc后初始化一个HeapFile对象,代表存储在some_data_file.dat的表将表加入catalog中。正在运行的数据库服务器会加载这个catalog信息
以上为数据库初始化的过程
创建一个查询计划(只用到
SeqScan操作符),从磁盘上扫描tuple 。一般而言,实例化的操作符需要引用相应的表(如果操作符SeqScan)或子操作符(如果操作符是Filter等)。测试程序在SeqScan运算符上反复调用hasNext和next,以逐个获取tuple。在扫描过程中,数据先尝试从bufferpool中的page读取,找不到的话再通过HeapFile对象从磁盘读取上面的代码文件应当创建在
src/java/simpledb目录下,并将some_data_file.dat文件放在top level dir中。运行命令以生成包含test.java的jar文件1
2ant
java -classpath dist/simpledb.jar simpledb.test

